∞ generated and posted on 2016.08.26 ∞
Post-duplication double helix, particularly but not necessarily exclusively as depicted during metaphase.
Sister chromatids are pictured especially as one-half of each metaphase chromosome. As such, they represent one daughter chromosome as seen in their metaphase, condensed form. They are called "sisters" because they represent one of two "daughter chromosomes".
The underlying daughter double helix exists immediately post DNA replication, but this is as chromatin rather than as a condensed chromosome. As such, you cannot describe one sister chromatid as having been derived from "Mom" and the other from "Dad" since, except for mutation, the two chromatids making up a sister chromatid pair are identical. They both were derived, that is, from the replication of the same double helix.
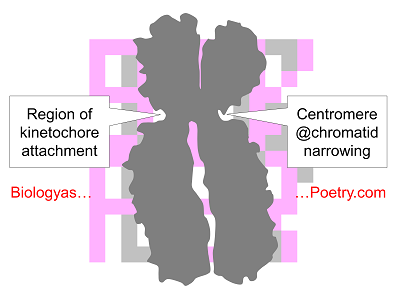
Figure legend: Depiction of metaphase chromosome indicating sister chromatids as well as location of centromere, which also is the site of kinetochore attachment. Chromosome image is based on trace of photograph posted on cytochemistry.net.
A metaphase chromosome consists of two sister chromatids forming a sister chromatid pair. An individual sister chromatid, during metaphase, is not an individual chromosome; instead it is the sister chromatid pair during metaphase that in turn is an individual chromosome.
Why? Part of the reason is that the concept of chromosome and that of double helix are not identical, particularly with the concept of "chromosome" historically having coming into existence long before that of "double helix". Thus, a chromosome is an independent entity as viewed through a light microscope and sister chromatids during metaphase are not independent entities but instead are attached at their common centromere.
At the start of anaphase the sister chromatids are separated. At this point each sister chromatid is indeed considered to be a separate chromosome. During anaphase a sister chromatid pair is converted into two separate sister chromatids and each chromosome (sister chromatid pair) is converted into two separate chromosomes (two separate sister chromatids). During all of this, however, a sister chromatid consists of one double helix, plus associated proteins.