∞ generated and posted on 2016.08.22 ∞
Relatively large biological molecule that mostly does not dissolve in water.
Lipids include fats, oils, cholesterol, a number of steroid hormones, the major constituents of cell membranes, etc.
Lipids are predominantly hydrophobic substances, though can have hydrophilic portions as well. An example of the latter are lipids associated with membranes, that is, lipid bilayers, include phospholipids and the molecule, cholesterol.
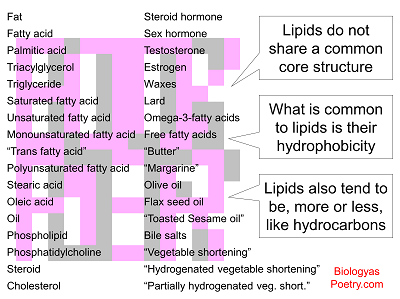
Figure legend: A diversity of lipids, some familiar, others less so.
Unlike proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids, lipids are less homogenous in terms of their structures. In particular, lipids do not have a consistent subunit from which they are polymerized but instead are categorized together as a group based upon their relative inability to dissolve in aqueous solutions. That is, they are oil-like in the generic sense of that term.
The following is a list of terms associated with lipids:
Cholesterol, Fat, Fatty acid, Glycerol, Lipid, Lipid A, Lipid bilayer, Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), Oil, Phospholipid, Saturated fatty acid, Steroid, Triglyceride, Unsaturated fatty acid
The following video provides a nice introduction to lipids: